- 3min
- 7240
- 0
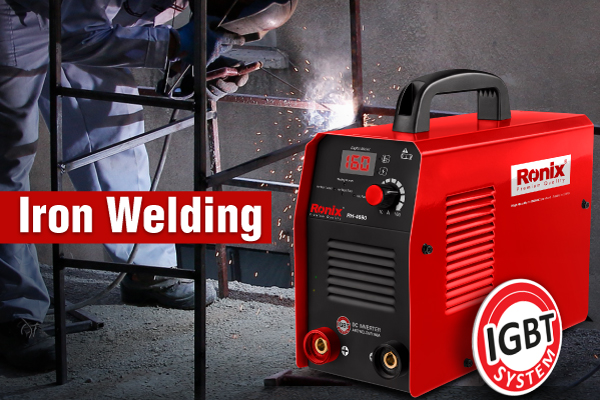
Iron Welding is a special process by which two homogeneous or non-homogeneous metals are linked locally and permanently joined together using or without the consumable metal and with or without melting.
Welding operation is a very precise and complex operation, because in most cases welding connects the vital parts of a structure and if the operation is performed incorrectly, separating the iron members and breaking a structure might be very difficult. Welding is used for many applications, not only to connect two iron objects, but also to repair lost or broken parts of a structure. This is done by a professional welder because only an experienced welder knows the basics of iron welding properly. Welding is also performed in different ways and in different stages. In the following, you will be familiar with types of welding and the advantages each could have.

Types of welding
Welding processes are divided into two general types as follows:
- Fusion Welding
- Solid-State Welding

Fusion Welding Process
Fusion Welding refers to the process through which the base metals are bonded by melting. In other words, the connection is made by melting the edge or surface of the parts and creating a local fusion. This group of processes is used not only for bonding metals but also for plastics and ceramics and is sometimes known as mixed welding.
The energy source in this type of process can be electrical or chemical. According to AWS A3.0 standard, Shield Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) process, is an example of a fusion welding process with an electric energy source and an Oxy-fuel Welding (OAW) process, is an example of these processes with a chemical energy source.
Advantages of fusion welding processes
- It is possible to use most of the processes of this group for welding parts and assemblies with different designs and situations.
- Possibility to use most of the processes of this group at the project site.
- It is possible to use most of the processes in this group to connect thick parts using chamfering and multilayer welding.
Solid-State Welding Process

Solid-State Welding process involves the process of bonding base metals by heating them to a paste level or by other means such as pressure. The energy source in this group of processes can be electrical, chemical or mechanical. According to AWS A3.0 standard, Induction Welding process (IW) is an example of Solid Welding Processes with Electric Power Source, Explosive Welding Process (EXW) is an example of these Processes with Chemical Energy Source and Friction Welding Process (FRW) is an example of these processes with a mechanical energy source.
Advantages of Solid-State Welding Processes
- Non-melting of the base metal in this group of processes causes a significant reduction in improper structural changes, especially in the heat affected area.
- Non-melting of the base metal in this group of processes eliminates the need to protect the molten pool and thus the emergence of related defects.
- Connections in this method receive less input heat, distortion and residual stresses.
- This method is suitable for producing a large number of welded assemblies and is economical.
- This group of processes is often Mechanized or Automatic using a welding machine operator. This makes the welding quality relatively independent of mistakes or even human skill.
Ronix
10 March 2021









