- 10min
- 35856
- an opinion
The Brushless DC motor revolutionized the electric propulsion industry. They have become the go-to solution for their impressive toughness, efficiency, and sleek design. This article is your friendly guide into the world of these cool motors, breaking down their details, different types, diverse uses, and delving into the reasons why they’ve become essential in an extensive range of everyday technologies.
What Is a Brushless Motor?
A brushless motor, often abbreviated as a BLDC motor, or BL, is an electric motor powered by direct current (DC) that stands out for its unique design. What makes them so special? Well, to answer that question first we need to ask an important question: what does brushless mean? Unlike traditional brushed motors that rely on mechanical brushes and a commutator, brushless motors operate without these components, leading to a host of advantages. Why are brushless motors better? Well, despite their higher initial costs, these motors prove to be more cost-effective in the long run, making them a preferred choice in various applications.
In today’s tech-driven landscape, brushless electric motors have emerged as the preferred choice for critical applications. They find a home in computer disk drives, where precision and reliability are paramount. Additionally, industries like robotics and aviation benefit from the characteristics of BLDCs, as they eliminate the need for a physical commutator.
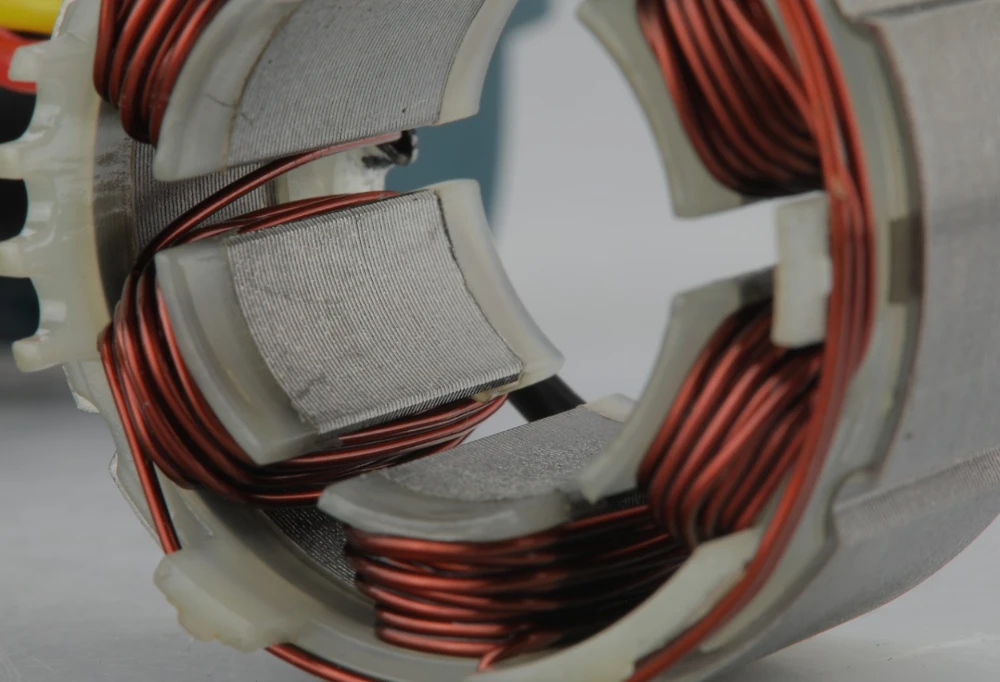
History of Brushless Motors
The origin of the brushless DC motor dates back to 1962 when T.G. Wilson and P.H. Trickey invented the first one, rightly named a “DC machine with solid-state commutation.” This milestone emerged from the rapid advances in solid-state technology during the early 1960s. Initially, these motors faced limitations in power generation, despite their durability. It wasn’t until the 1980s when stronger permanent magnet materials became available, paving the way for Robert E. Lordo to produce the first large-scale brushless DC motor. This breakthrough marked a tenfold increase in power compared to its predecessors.
The history of the DC brushless motors is a journey marked by innovation, overcoming challenges, and continuous improvement. From the pioneering work of Wilson and Trickey to Lordo’s groundbreaking developments, the evolution of brushless DC motors has paved the way for more efficient, reliable, and versatile technologies. As industries continue to evolve, the story of brushless motors unfolds as a testament to human ingenuity and the pursuit of excellence in electric movement.
How Do Brushless Motors Work?
Making Magnetic Magic: Rotor and Stator’s Role
Picture the rotor and stator as dance partners. The stator, with its winding, creates a magnetic field, pushing the rotor to move. This magnetic action happens when we give power (voltage) to the stator coils in a three-phase pattern.
Controller’s Job: Keeping the Dance in Sync
Now, here’s where the controller takes the lead. It makes sure the right coils get power at the right time. This is crucial for the rotor to spin correctly. Sensors, like Hall sensors, help the controller know where the rotor is.
Stator’s Skills: Single to Three-Phase Configurations
The stator is like a superhero with different outfits. It can have one, two, or three phases in its winding, making it flexible for various jobs.
In a nutshell, to give an answer to the question of what is a brushless motor and how does it work, we can say that it works by creating a magnetic dance between the rotor and stator, guided by a smart controller and sensors. This makes them reliable and adaptable for all kinds of tech wonders we use every day.
Related Article: Brushless Vs. Brushed Motors
Brushless Motor Types
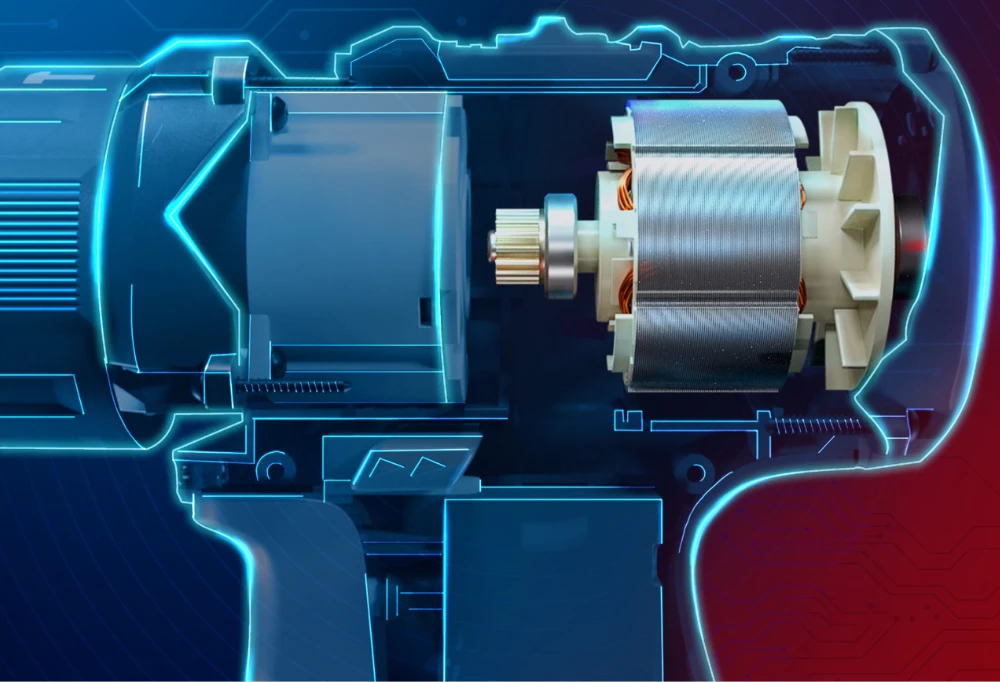
What Are Brushless Motors Used For?

BLDCs perform many duties that brushed DC motors used to take care of, but high price tags and the control complexity have prohibited BLDCs from totally replacing brushed motors in all sectors. However, they have grown to dominate numerous fields, including computer hard drives and CD/DVD players. BLDCs are used exclusively to power small cooling fans in electrical devices. A 12v brushless motor is a great choice for home appliances and light-duty power tools while the 18 and 20 versions are used for more heavy-duty applications.
These efficient motors are common in cordless power tools, where the improved motor efficiency allows for extended durations of usage before the battery has to be recharged. Direct-drive turntables for gramophone records employ low-speed, low-power brushless motors.
Many current cordless tools run on a brushless DC electric motor, including string trimmers, leaf blowers, circular and reciprocating saws, and drills. These sources of power have more benefits over brushed ones (low weight, high efficiency) for portable, battery-powered equipment than for big, stationary tools plugged into an AC outlet, hence adoption has been faster in that part of the market.
Types of Brushless Motors
Brushless motors, like a diverse cast in a tech play, come in different types, each with their unique strengths. Let’s take a quick peek into this motor range:
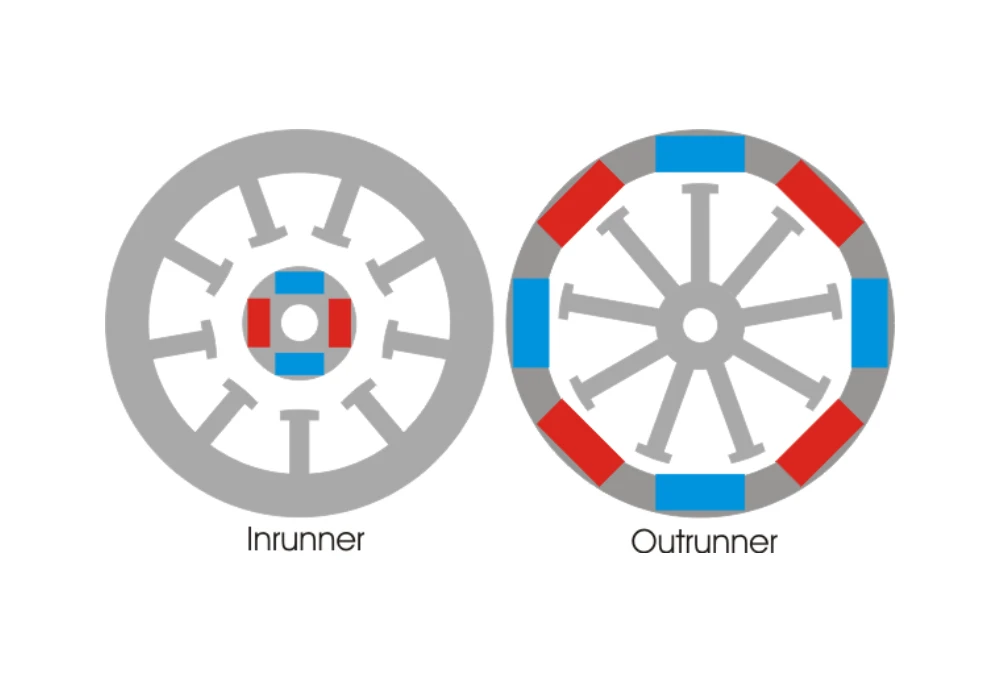
1. Inrunners: Precision in a Compact Package
Inrunner motors are like the precision artists of the group, with the stator tightly wrapped around the rotor. Perfect for applications needing accuracy in a small space, like RC cars or certain industrial setups.
2. Outrunners: Power Unleashed in Rotation
Outrunners are the powerhouse performers, with the rotor surrounding the stator. Think drones and applications where power and efficiency take the stage.
3. Coreless Brushless Motors: Light on Their Feet
Coreless motors are the lightweight sprinters, shedding the iron core for swift movements. Ideal for applications demanding speed, like high-speed robotics or certain medical devices.
4. Steppers: Dance to Precise Steps
Stepper motors are the choreographers, moving in precise steps for applications demanding accuracy, such as 3D printers and CNC machines. They follow digital pulses, ensuring controlled and predictable moves.
5. Servos Brushless Motors: Precision with a Feedback Beat
Servo motors are the precision maestros, delivering accuracy through feedback control systems. Found in robotics and automation, they ensure spot-on position control.
6. Synchronous Brushless Motors: Synchronized Strength
Synchronous motors are the synchronized performers, keeping the magnetic field and rotor’s movements in harmony. Think of appliances and devices where consistent performance is key.
Understanding these motor buddies ensures picking the right one for the tech gig. Whether it’s precision, power, or simplicity you’re after, there’s a brushless motor ready to shine in every role.
Brushless Motor Sizes
Brushless motors, designed to fit a variety of tasks, come in two primary sizes: small and large. Each size serves specific needs, contributing to the efficiency and functionality of various applications.
Small Brushless Motors: Compact Yet Capable
Small brushless motors may be compact, but they are versatile and powerful. These miniature wonders find their place in precision-demanding applications, showcasing their ability in gadgets like tiny drones and precise medical devices. Despite their modest size, small brushless motors play a significant role in enhancing the agility and functionality of portable and precision-oriented technologies.
Large Brushless Motors: Powering the Heavy-Duty
On the flip side, large brushless motors step into the scene as robust workhorses, handling heavy-duty tasks with ease. Their considerable size and strength make them essential for applications requiring raw power and endurance. Picture them thrusting electric vehicles, driving the machinery in industrial settings, or ensuring the operation of large-scale automation systems. The brawn of large brushless motors positions them as the backbone of numerous industrial and transportation applications.
In summary, brushless motors offer a size spectrum providing for various tasks, from the complicated precision of small motors to the raw power of larger ones. This diversity ensures that there’s a brushless motor size perfectly suited for every job, big or small.
What Are the Advantages of Brushless Motors?
1. Smooth Operator:
Features a linear mechanical setup, offering a smooth speed ride from slow to fast and everywhere in between.
2. Torque Talk:
Talks the torque game with good power at middle and low speeds, a strong kickstart, and the ability to handle heavy loads like a champ.
3. Gentle Start, Gentle Stop:
Starts and stops with finesse, unlike brushed motors.
Respects the classics with the option to keep the original brake mechanisms intact.
4. Spark-Free Performance:
No sparks here! Thanks to no brush friction, it’s cool, literally.
5. Trusty Sidekick:
A reliable companion, always stable, flexible, and low-maintenance, reducing the stress on your tech team.
6. Compact and Light:
Small but mighty! Takes up less space and weight but still packs a punch.
7. Tough Nut:
Resilient against bumps and shakes, keeping things smooth and quiet. Long life? Absolutely!

What Are the Disadvantages of Brushless Motors?
As many advantages Brushless motors have there also are a number of drawbacks to them:
1. Cost Hurdle:
It’s the real talk—building these fancy motors can cost a bit more upfront.
2. Complexity Chronicles:
Sometimes, being too fancy can be tricky. More complexity means a slightly higher chance of things going a bit haywire.
In a nutshell, brushless motors bring a lot to the table, from smooth rides to reliability. Just be aware of the upfront costs and the complexity dance – it might be worth it, depending on your tech party’s vibe and budget plans!

What is the Best Option, Brushed or Brushless?
Since way back in 1856, brushed DC motors have been doing their thing in different jobs, from making things move to running big machines. But now, we’ve got a new player in town: brushless DC motors with electronic speed controllers. These guys are the real winners for a few reasons. They work great in things like robots and medical gear because they can spin fast and don’t get too hot. Plus, they last way longer than the old brushed ones, making them perfect for stuff that needs to keep going without a lot of fuss. So, when it comes to picking the best motor, the brushless ones take the crown, especially for important machines and cool robots.
The ones with brushes usually clock out after around 1,000 to 3,000 hours – that’s their average time. Now, the brushless DC motors? They’re the endurance champs, going strong for tens of thousands of hours! So, if you’re looking for a motor that’s in it for the long haul, the brushless crew is where the durability party’s at.
FAQ ❓
Is A Brushless Motor Really Better?
Yes. Brushless motors are more durable and efficient than brushed ones. They have a longer lifespan, produce less noise, and require less maintenance.
What Are the Different Types of Brushless Motors?
There are two types of brushless motors: Inrunner and outrunner. In the inrunner models, the rotor is at the center encircled by the stator winding while in the outrunner ones, the rotor surrounds the winding.
Ronix
13 December 2021









You need to be a part of a contest for example of the most useful blogs online. I am going to suggest this web site!