- 12min
- 83509
- an opinion
If you’ve ever seen sparks coming from a power drill’s motor cooling vents, you’ve seen Electric Brushed Motors in action. They are widely used motors, basically applied in different industries, ranging from the realm of electrical propulsion, cranes, and paper machines, to steel rolling mills.
They work as follows: The arcing is caused by electricity being carried from the stator, which is the nonrotating component of the motor, to the armature, which is the spinning part. Brushes are the parts of an electric motor’s stator that conduct the current to the rotor. But what are the Carbon brushes and what do they exactly do? and What is a brushed motor? How does a brushed motor work?
Let’s get into the first question:
What Is A Carbon Brush?
A carbon brush is a sliding contact used in Brushed Motors and generators to transport electrical current from a static to the revolving part while assuring commutations with fewer sparks.
It is made up of one or more carbon atoms. One or more shunts and terminals are included. Brushes are made from five different brush-grade families, including Carbon Graphite, Electrographite, Metal Graphite, Silver Graphite, and Carbon Composite. Each one is tailored to a specific need and has its own manufacturing method. But How do they operate?
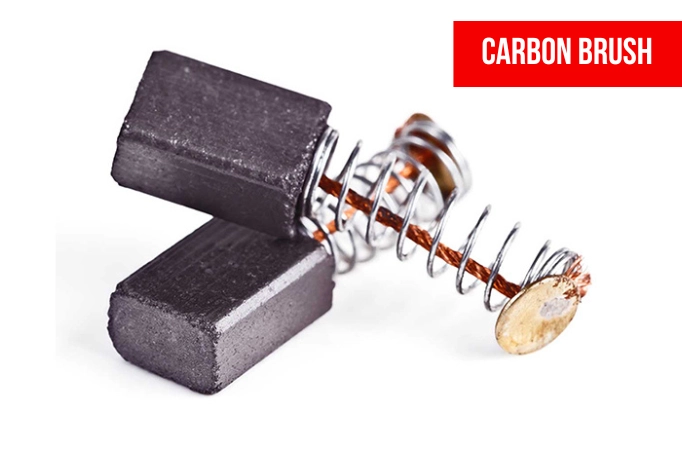

Brushes’ Operating Parameters:
In the operation of electrical machinery, the carbon brush is crucial. We must consider three sorts of parameters in order for it to do its function:
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Physical and chemical
Electric motor brushes are selected based on the tool’s brand and kind. They are put on the permanent portion of a motor (the Stator) to guarantee that power is transmitted to the rotor as efficiently as possible. They allow for switching without the need for a spark.
The slip rings are permanently in touch with the carbon brushes. These graphite components come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They might have a spring, a connection (a wire with a plug), or no brush holder at all. Brushed Motors come in a variety of sizes and forms (often square and rectangular) and may contain grooves to aid in direction.
Carbon brushes are spring-loaded and fastened to a spring with a plate to guarantee that power is passed smoothly. In certain circumstances, the brushes are held in place by a brush holder with a spring designed to increase force.
Brushes that are compatible with portable power tools, such as drills, are normally sold by the manufacturers. The thickness, depth, and breadth of the item are measured in millimeters or inches, respectively. These specs, however, may differ from one manufacturer to the next.
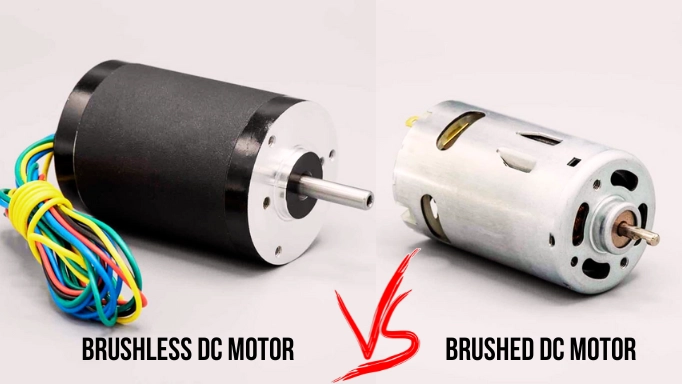
What is a Brushed DC motor?
Any specialist in motion control should be able to distinguish between brushed and brushless DC motors. Previously, brushed motors were fairly prevalent. Though brushless DC motors have nearly replaced them, the correct DC motor of either type may make a project significantly more efficient.
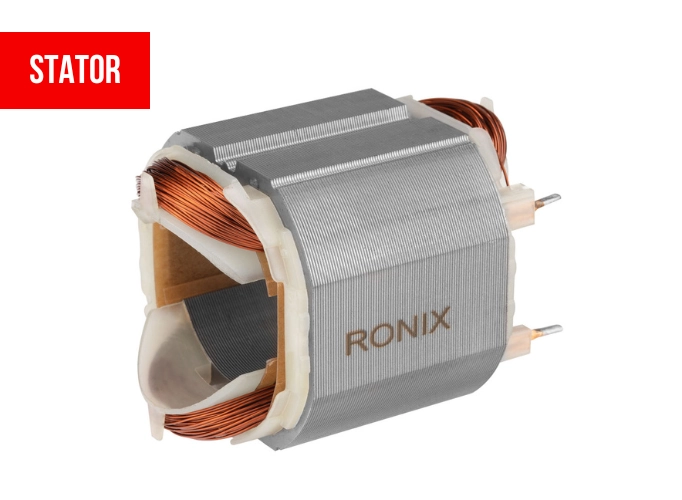
The following are the major components of a brushed DC motor:
- Stator—a permanent magnet-encased enclosure.
The armature is a rotor with a number of electromagnets installed on it. Inside the stator, it spins freely.

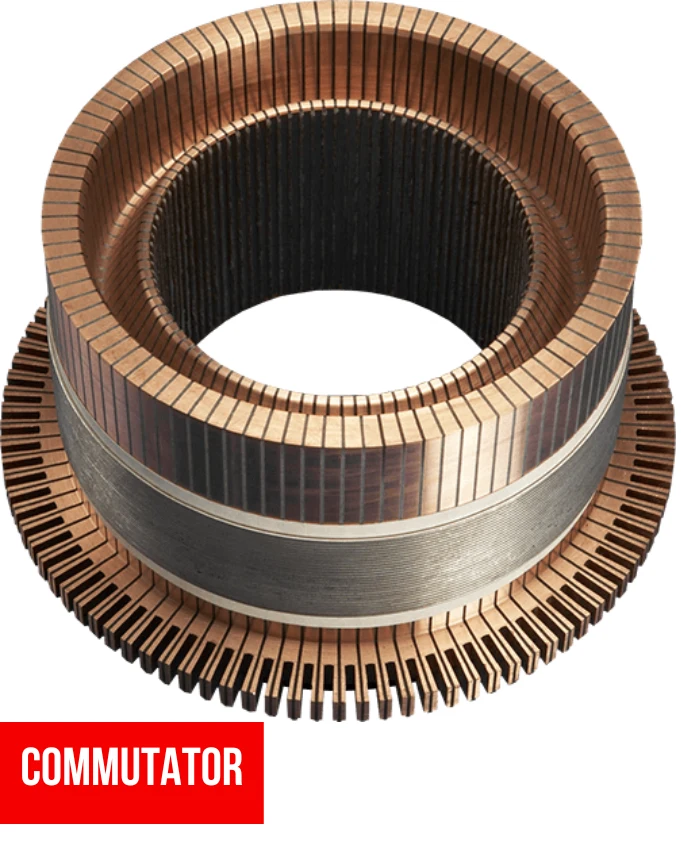
- Commutator— A metal ring attached to the armature shaft is known as a commutator.

- Brushes— To maintain electricity flowing to the armature coils, carbon slabs remain in contact with the commutator.
What Do Brushes Do in Electric Motors?
In Brushed DC Motors, when electricity is applied to the electromagnet in the armature, a magnetic field is created that attracts and repels the magnets in the stator. The armature rotates in a 180-degree circle. To maintain the electromagnet spinning, the poles must be swapped. The Carbon brushes are in charge of polarity shifts. They contact the armature’s two rotating electrodes. The magnetic polarity of the electromagnet is reversed as it rotates.
But, why carbon brushes? What is the specific quality that makes them a good fit for electric motors?
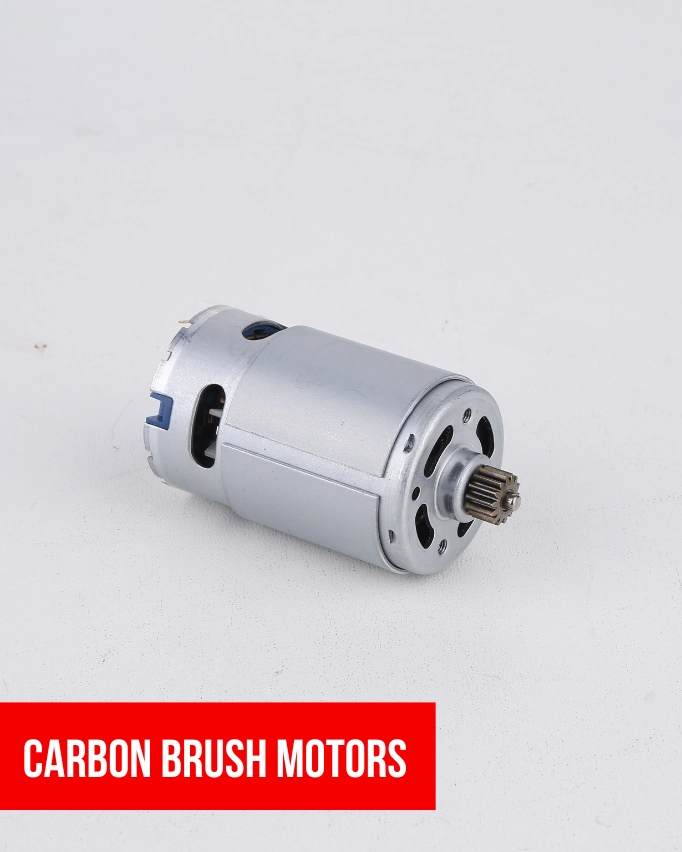

Why ‘Carbon’ Brushes Are Used in Electric Motors?
Carbon brush motors are used in electric motors due to their excellent electrical conductivity, low friction characteristics, self-lubricating properties, good thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness.
They facilitate efficient electrical current transfer between the stationary and rotating components of a motor, minimize wear and tear, dissipate heat effectively, and have a low wear rate, resulting in longer motor lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. Their versatility and ability to form a self-lubricating film on the contacting surfaces make them a practical choice for various types of electric motors and applications.
Afterwards, Let’s take a look at it more visually.
Brushed Motor Diagram
Here you can see the structure of in a brushed motor diagram.

Then let’s answer a common question:
Do AC Motors Use Brushes?
No, there is no AC Brushed Motor out there. Unlike brushed DC motors, which rely on physical brushes and a commutator to transfer electrical power to the rotating armature, AC motors operate differently. AC motors, such as induction motors and synchronous motors, work by inducing a rotating magnetic field within the stator, which interacts with the rotor to generate motion. So, there is no need for brushes and the associated wear and maintenance issues found in brushed DC motors.
But, what about the brushless ones? what makes them different from the brushed ones?
What’s the Difference Between Brushless and Brushed DC Motors?
The armature, which is made up of wrapped wire coils, acts as a two-pole electromagnet in a DC Motor with Brush. The commutator, a mechanical rotary switch, reverses the directionality of the current twice every cycle. As a result, the electromagnet’s poles pull and push against the permanent magnets along the exterior of the motor, allowing electricity to flow more freely through the armature. As the commutator’s poles cross the permanent magnets’ poles, the armature’s electromagnet’s polarity is reversed.
On the other hand, a brushless motor has a permanent magnet as its rotor. It also employs three stages of driving coils as well as a unique sensor that monitors rotor position. The sensor delivers reference signals to the controller as it tracks the rotor position. The coils are then activated in a systematic manner by the controller, one phase after the other.
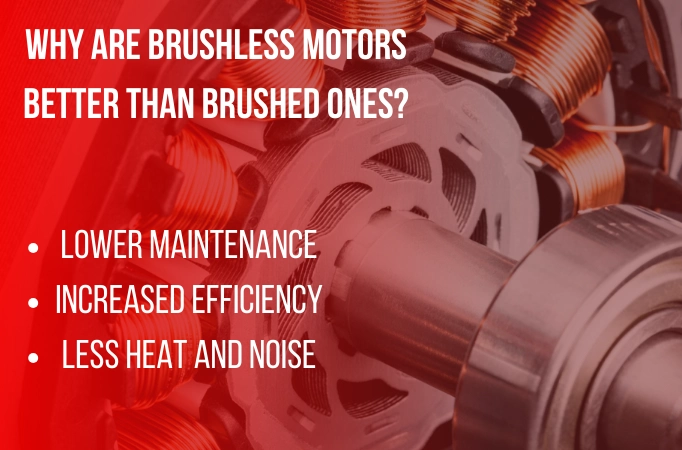
Which Is Better?
In general, brushless motors outperform DC brushed motors. Users can benefit from lower maintenance, increased efficiency, and less heat and noise. Brushless motors have one or more permanent magnets and are synchronous. Brushless motor power tools are currently considered high-end items.
Why Are Brushless Motors More Expensive Than Brushed Motors?
The rotor (the machine’s revolving portion) is powered within the stator in a traditional DC motor with brush (fixed part). The collector or commutator, which is in touch with tiny carbon brushes, connects the two via an electrical connection.
The rotor in brushless technology is made up of magnets, whereas the stator is made up of coils that are alternately charged positively or negatively. As a result, the poles attract and repel each other, allowing the motor to rotate.
The advantage is that the rotor and stator do not make physical contact. Electromagnets use magnetism to transfer energy from one to the other.
The motor is powered by direct current and runs on an alternating current generated by an electronic card that converts the direct current into a three-phase variable frequency. As a result, the coils are alternately supplied, resulting in a rotating field and consequently spinning. The electronic module, which is either incorporated into the motor or housed in a housing, constantly adjusts the current to ensure that the motor runs at optimal efficiency. As a result, overall performance improves, and you get more bang for your buck.

Do Brush Motors Have More Torque?
Brush motors can perform well when providing an initial torque, but they usually fall short when great torque is required, because their commutation system is so simple. Hence, brush friction increases as speed increases and viable torque decreases. In this case, they are less efficient in comparison with brushless DC and AC induction motors. But how to make them faster?
How to Make A Brushed Motor Faster?
By adjusting the operating voltage or the intensity of the magnetic field in the Brushed DC Electric Motor, using brushed motor driver, the speed and torque may be adjusted to give a constant speed or a speed that is inversely proportional to the mechanical load. (The controller sends current pulses to the motor windings, which govern the motor’s speed and torque.)
Additionally, some advanced brushed dc motor driver offers feedback control and optimized settings to fine-tune torque output. Consulting the motor and driver documentation is crucial for safe and effective torque adjustments.
However, why should users use brushed motors despite the low speed? What are the benefits? Are there any drawbacks by the way?
Benefits of a Brushed Motors DC
- Overall construction expenses are low
- Rebuilding is a common way to extend the life of a product
- They are simple and low-cost controller
- For fixed speed, no controller is required
- They are ideal for use in harsh operating conditions
The Drawbacks of a Brushed Motors DC
- They are Less effective in comparison with brushless motors
- Their commutators’ switching motion causes a lot of electrical and electromagnetic noise by continually building and breaking inductive connections
- Brushes and commutators wear out because they are in constant direct contact with the shaft.

DC Motor Brush Replacement
Electric motor brush replacement extends the life of motors and equipment. First, ensure safety by disconnecting power and wearing appropriate gear. Access the brushes by removing covers or panels, then identify and disconnect the wires attached to the old brushes.
Gently remove the old brushes using pliers or a screwdriver. Inspect them for wear and damage. Slide new carbon brushes into the holders, ensuring a secure fit, and reconnect the wires. Reassemble the equipment, test it, and monitor for proper operation.
Uses of Brushed DC Motor
In home products and autos, brushed DC motors are still widely utilized. They also have a large industrial following due to the ability to change the torque-to-speed ratio, which is only possible with brushed motors.
Conclusion
What we can say about DC brush motor in a brief now is that a brush is an electrical contact that transfers electricity from stationary wires to moving elements, most typically in a rotating shaft. Electric motors, alternators, and generators are examples of typical uses. The lifespan of a carbon brush is determined by how frequently the motor is used and how much power is applied to it. Carbon brushes are one of the most inexpensive components of an electric motor. On the other hand, they are frequently the critical component that ensures the motor’s longevity (“life”) and performance. Their manufacturing necessitates a high level of quality control and production process control at all stages of the process. Then if you want to find tools with brushed motors, or simply want to have access to a bank of spare parts including high quality brushes, you can all in all rely on Ronix Tools.
With over 2000 tools and 34000 spare parts, Ronix can provide you with whatever you need asp.
FAQ of Everything You Need to Know About Brushed Motors
What is Brushed DC motor?
One of the most basic forms of DC motor is the brushed DC motor. Mechanical commutation is used to transmit current to the motor windings through brushes.
Where do brush dc motors are used?
Brush dc motors, on the other hand, provide high peak torques and may be driven by simple speed controllers to move a wide range of applications. They are frequently less expensive than alternative options, especially in big quantities. They can also have a linear torque-speed connection, which simplifies control.
What distinguishes a brushed from a brushless motor?
Brushless motors have three wires, whereas brushed motors have two. Brushless motors do not have brushes, but brushed motors have. You may also know by inspecting the motor.
How do brushed DC motors work?
Mechanical switching is used in brush dc motors to alter current polarity across the armature windings (and let the armature continue smooth rotation). The commutator is a mechanical switching assembly (usually composed of copper). A brush (made of carbon, metal, graphite, or a mix of materials), a shunt and spring, as well as a brush positioner and connections, make up the brush assembly that interacts with the commutator.
Ronix
13 December 2021








Comfortabl y, the post is really the freshest on that deserving topic. I harmonise with your conclusions and also will thirstily look forward to your next updates. Just saying thanks will certainly not simply be acceptable, for the extraordinary clarity in your writing. I will directly grab your rss feed to stay informed of any updates. Gratifying work and much success in your business dealings!
I got what you mean , thanks for posting .Woh I am happy to find this website through google.