- 8min
- 20476
- 0
Choosing the right constant speed motor is like picking the perfect superhero for your mission—it’s got to match the application, deliver the required functions, and have the right power. Imagine it’s a motor Avengers assembling for your specific needs!
The process of selecting a motor and gearhead should begin with a thorough examination of the motor’s specifications to ensure that the motor you choose meets the application’s requirements. What you need to begin your selection is some factual and useful information about the motors. The constant-speed electric motor combines an induction motor with a power-on activated type clutch and brake. It’s perfect for frequent start-and-stop operations. Suitable for situations where the motor is run at a synchronous speed independent of load torque and the motor is started, stopped, and reversed frequently.
Different Types of Industrial Motors
In the big world of motors used in industries, there are mainly two types: AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current).
While there are many different motor types, there is a lot of overlap in industrial applications, thus the market has pushed for motor selection to be simplified.
Among these, motors that keep a steady speed, known as constant speed motors, are really important for many jobs. Brushless DC motors, for instance, are great for tasks where keeping a consistent speed is crucial.
Other motors like brush DC, AC squirrel cage, and wound rotor motors are also good at maintaining a steady speed. They are used in various industries, from running machines in factories to helping with automated processes.
Servo motors are precise and can adapt to changes, making them useful where a constant-speed motor is needed. Stepper motors are good for situations where exact control of rotation is necessary. While there are some motors designed for specific jobs, the six types mentioned, especially those that keep a constant speed, are versatile and reliable for most tasks in industries. Their ability to work predictably and steadily makes them important for many processes that rely on motors.
And guess what? There’s another hero in this lineup – the motor with constant speed. This special one is like the steady and reliable friend that keeps things running smoothly, especially when you need a consistent speed. While some motors are used for specific jobs, the constant-speed motor is like the all-around champion, fitting well into most tasks in industries, making it a reliable choice for many jobs.

What are Constant Speed Motors?
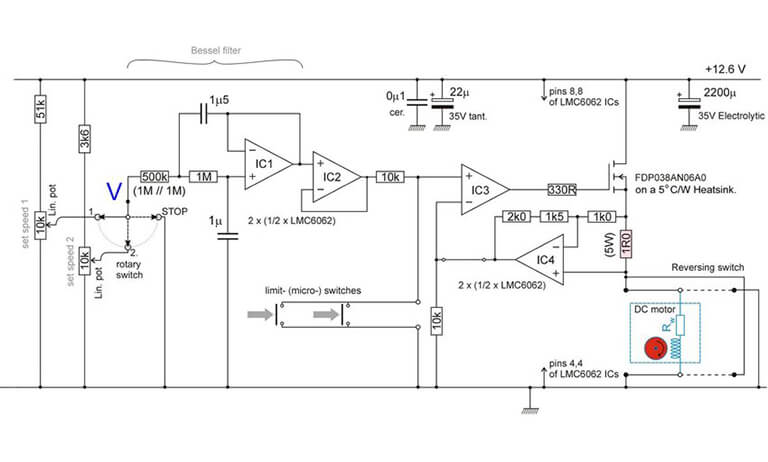
Motor with Constant Speed is like the rockstar of electric motors—they keep their cool and maintain a pretty consistent speed during regular operation. Think of them as reliable performers that stick to their rhythm. Examples include synchronous motors, low-slip induction motors, or your regular DC motors with parallel windings.
In this case, you can call an induction motor, which is defined as a constant speed motor. The rotor flux rate lags slightly behind the stator flux and there is a relative velocity between the stator and the rotor. The difference in engine speed changes slightly with increasing engine load. In a vacuum, this is called sliding speed. There is very little slip at idle and the torque generated by the engine matches idle and friction losses. Consequently, at idle speed, the motor rotates at almost synchronous speed (Ns = 120f / P).

Are constant speed motor AC or DC?
Constant speed motors can be either AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current).
AC Constant Speed Motors
- Synchronous Motors: These motors operate at a speed that synchronizes with the frequency of the AC power supply. They are known for their precise speed control and are commonly used in applications where a constant speed is essential.

Low-Slip Induction Motors: While most induction motors exhibit some slip (difference between synchronous and actual speeds), low-slip induction motors are designed to minimize this slip, providing relatively stable speeds.
DC Constant Speed Motors
- DC Motors with Parallel Windings: Certain types of DC motors, particularly those with parallel windings, are designed to maintain a constant speed. These motors are suitable for applications requiring consistent and predictable rotational speeds.
- Brushless DC Motors: Brushless DC motors, while not inherently constant speed, can be electronically controlled to maintain a steady speed in various applications.
📌When the load increases, the motor tries to transfer the load to the mechanical load, and in this process, the motor speed decreases. Decreasing the motor speed causes slip to increase and the motor draws a large current from the rotor to transmit torque, which tends to return the motor speed to its original speed.
The slip of the induction motor ranges from 3% to 5% of the synchronous speed. As the inductive load increases, the slip decreases within the specified slip range. Therefore, an induction motor can be called a constant-speed motor.
Constant-Speed Application, a Constant-Speed Motor
In a constant-speed application, a motor typically runs at a constant speed, with little or no regard for acceleration and deceleration ramps. Across-the-line on/off control is commonly used in this sort of application. A branch circuit fusing with a contactor, an overload industrial motor starter, and a manual motor controller or soft starter are common components of control circuits.
📌 For constant speed applications, both ac and dc motors are acceptable. DC motors have a large installed base and offer full torque at zero speed. AC motors are also a suitable alternative due of their high-power factor and low maintenance requirements.

What Is the Difference Between Constant Speed and Double Speed Tools?
- One main difference is the gearbox design. Constant speed tools provide maximum speed and power, but dual speed tools can be configured for two modes: fast and slow.
- Working with a two-speed tool is more efficient. On the contrary, a tool with a constant speed provides a lot of power and is very convenient for projects that require a lot of effort.
- A double-speed tool can be used for various types of work, but a constant-speed device has been designed for a special purpose. For example, a double-speed drill is used for drilling, impact drilling and wrapping. But ordinary drills are only suitable for drilling operations.
- The versatility of single-speed tools is much less than that of two-speed tools, even if the power is the same.
the application of constant speed motors in the tools industry
Constant speed motors find various applications in the tools industry due to their ability to maintain a stable speed regardless of load variations. Here are some common applications in the tools industry:
Power Tools: Many power tools, such as electric drills, grinders, and circular saws, require a constant speed for optimal performance. Constant-speed motors ensure that these tools maintain a consistent rotation speed, providing efficiency in various tasks.
woodworking tools: Woodworking tools like routers and planers rely on constant speed motors for optimal performance. Maintaining a consistent speed is essential in achieving smooth and uniform cuts in wood, and these motors play a key role in sustaining the desired cutting speed throughout the woodworking process.
Metalworking Tools: Tools used for metal fabrication, such as metal grinders and polishing machines, often incorporate constant-speed motors. This ensures that the tools operate at a steady speed, providing quality finishing and shaping of metal surfaces.

FAQ
What do you call a constant-speed motor if you don’t know what it’s called?
A shunt motor is a direct current motor having two parallel windings that have the same voltage across them. Induced voltage is proportional to speed in a shunt motor, and torque is proportional to armature current.
Which DC motor has a constant rotational speed?
DC shunt motor always maintains a constant speed.
what are the applications of constant-speed motors in the tools industry?
Constant-speed motors in the tools industry are employed in power drills, grinders, sanders, routers, lathes, circular saws, precision cutting tools, and torque wrenches, ensuring consistent and accurate operation.
are constant speed motor AC or DC?
Constant speed motors can be either AC or DC, maintaining a steady rotation speed in operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric motors that exhibit a consistent and reliable operating speed, be it theoretically or practically, are recognized as constant-speed motors. This category encompasses notable examples such as synchronous motors, low slip induction motors, and conventional parallel winding DC motors. Understanding and utilizing these constant-speed motors play a pivotal role in various applications across industries, ensuring stability and efficiency in motor-driven processes.
Ronix
13 December 2021