- 9min
- 27423
- 0
Are you about to start a new career or a project dealing with precise measuring? Are you not sure which types of measuring tools you need to have before getting started? Well, look no further! We’ve accumulated a list of different measuring tools and you can find which tools need to be on your shopping list before starting the job. Let’s not waste any time and find out what you need.
Types of Measuring Tools and Their Uses
You probably don’t want us to name types of measuring tools like a laundry list. You have one or more specific applications in mind and you want to know what measuring tools you need for them. Or maybe, you want to make sure a type of measuring tool you already have on hand is suited for your job. So, let’s just let you in on the answers to your questions.
Measuring Tools List
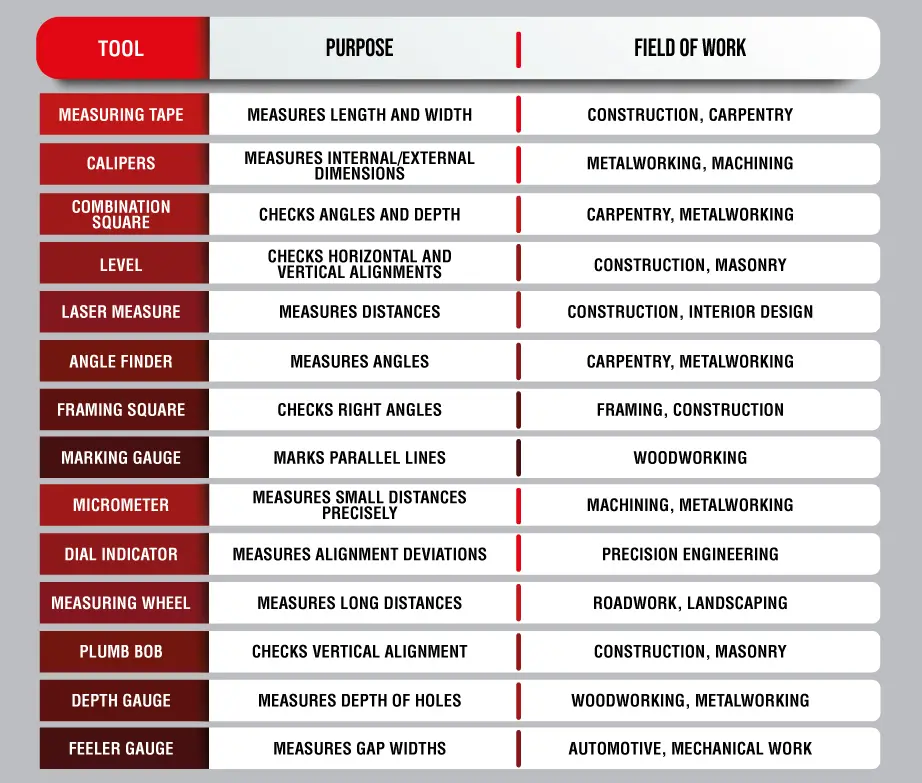
Here’s a table providing a list of measuring tools you’ll need to start or complete your task.
Types of Precision Measuring Tools
Our first stop is the precision measuring tools that are used for a wide range of jobs such as machining and fabrication, quality control, electronics manufacturing, laboratory experiments, mapping, medical uses, and many more. But why is it necessary to use precision measuring tools for these jobs?
Order Wholesale Measuring Tools Designed to Attract Customers

- Minimizing errors and waste
- Ensuring safety
- Repeatability and consistency
- Meeting industry standards
- Technological advancements
Okay. So, this is the reason why we need precision. But what measuring tools are considered precision ones?
Each of the tools in this list is used for:
Micrometers: Measuring very small distances (typically up to 1 inch) with accuracy showing measurements down to thousandths of an inch.
Calipers: Measuring distances between two opposite sides of an object. They can be vernier, dial, or digital.
Read more: Choose the Best Measuring Tools

Bore Gauges: Measuring the diameter of holes, bores, or cylinders.
Dial Test Indicators (DTI): Measuring the small linear distances or small variations in surface flatness.
Height Gauges: Measuring the vertical distance between a reference surface and a specific point on the object or feature being measured.
Depth Gauges: Measuring the depth of slots, holes, and recesses in a workpiece
Gauge Blocks: Also known as Jo blocks or slip gauges, precision-machined blocks of metal or ceramic are used for setting and calibrating other measuring instruments and making highly accurate measurements.
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM): Measuring the complex geometrical characteristics of 3D objects with high precision. Essential for quality control and product development.
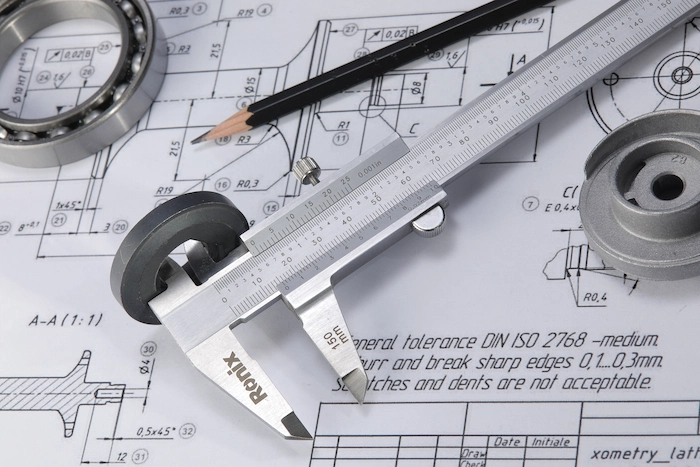
Laser Measurement Tools: Laser distance (Ronix RH-9150T) meters and laser scanners are used for distances and to create digital profiles of objects.
Our Suggestion: Ronix RH-9150T Laser Distance Meter 50m-Timer Countdown-Taiwan

Theodolites: Optical instruments for measuring angles in horizontal and vertical planes.
Total Stations: This tool combines a theodolite with an electronic distance meter for comprehensive measurements.
Micropipettes: For measuring and transferring very small volumes of liquid in biology labs.

Data Collection Systems: To collect, store, and analyze measurement data from various sources.
Squares and Precision Rules: Squares and precision rules to measure and mark straight lines, angles, and dimensions with high accuracy.
Protractors and Angle Measurements: To measure and draw angles
Machinist Precision Levels: To Check the flatness and alignment of surfaces and machinery.
Profilometers: For measuring surface texture and roughness
Read more: Best Measuring Tools for Woodworking

Fixed Gage Standard: Also known as reference standards or master gages are used to calibrate and verify the accuracy of measuring instruments.
Dividers and Trammels: To mark and transfer precise measurements or distances onto workpieces.
Types of Measuring Tools for Workshops
Different tasks get done in a workshop and each requires different types of measuring tools. So, you need different sets of tools for each. Let’s take a look.
For basic measurement functions, you need:
Rulers
Tape Measures: Ideal for longer distances and curved surfaces (Ronix RH-9030)
Folding Rules: Portable for projects on the go
Squares: Try and combination to ensure right angles, level, mark, and more
Protractors: for measuring and transferring angles
Idea pick: Ronix RH-9050 Measuring tape 3m

For marking materials, you need:
Marking Knives: For scribing precise lines on different materials
Center Punches: For creating small indentations to mark the drill starting point

Marking Gauges: For marking parallel lines at specific distances
Scriber: For marking lines on workpieces, finer than marking knives

For leveling and alignment, you need:
Levels: For making sure the surface is horizontal or vertical
Torpedo Levels: Compact levels for tight spaces

Some other types of measuring tools you might need are:
Thread Pitch Gauges: For identifying the thread size of screws, nuts, and bolts
Angle Finders: For measuring angles between surfaces
Types of Measuring Tools for Carpentry
Well, carpenters work in workshops so a great part of the measuring tools they use are in the list above. Besides those, they also use:
Carpenter’s Pencils: To provide a broader line that’s more visible
Bevel Gauges: To measure and replicate angles, especially irregular ones, for cutting and shaping wood
Angle Gauges: For measuring and setting angles accurately for miter cuts and joinery
Chalk Line Reels: For creating straight reference lines over long distances on wood
Framing Squares: Also known as carpenter squares, for framing and layout work
Carpenter’s Levels: Specifically designed for woodworking tasks with magnetic edges
Sliding T-Bevels: For transferring angles and making precise angle cuts
Carpenter’s Compass: For scribing arcs and circles on wood surfaces
Miter Square: For setting and marking accurate angles for angled cuts
Speed Square: Combines square, level, and marking features
Rafter Square: For laying out and marking roof rafters with a correct pitch or angle
Types of Measuring Tools for Plumbing
If you’re just starting a career as a plumber and you want to know which types of measuring tools you’re going to need at the beginning of your job, it’s your lucky day! But you don’t need to be a beginner for the following text to help you. The world of tools is expanding day-by-day and you need to update your toolbox now and then. Who knows, there might be a lot of different measuring tools out there that are going to make your life way easier. So, let’s find out about the world of plumbing life facilitators!
If you’re a beginner in plumbing, different types of measuring tools you need are:
Pipe Wrench: With scale for measuring pipe diameter

Torpedo Level: A small level suitable for checking the level on short runs and ensuring proper drainage slopes in pipes
Bubble Level: For leveling faucets or showerheads
Pipe Thread Gauge: For identifying the thread size and pitch of pipes and fittings
Pipe Cutter: With built-in scale
Tape Measure
Our recommendation: Ronix RH-9078 Measuring tape 7.5m-Omega model
Folding Rule
Marking Pencils
A tubing cutter with scale and a soapstone for marking pipes are optional but can greatly help you along the way.
And if you’re a professional plumber looking to upgrade your measuring game, keep these tools in mind:
Pipe Thread Gauge: For identifying the thread size and pitch of pipes and fittings to prevent leaks

Laser Level: Not essential but helps a lot with having precise alignments over longer distances
Pipe Benders: For bending pipes to specific angles without kinks or crimping
Pipe Fitting Gauges: To ensure proper fit between pipes and fittings
Plumb Bob: For establishing a true vertical reference line
Pressure Gauges: For measuring the pressure of liquids or gasses in plumbing systems
Flow Meters: For measuring the rate of fluid flow in pipes
Temperature Gauges: For monitoring the temperature of fluids in plumbing systems

Electronic Leak Detector (optional)
Depth Gauge
Types of Measuring Tools for Electrical Work
When someone is doing electrical work, being precise extremely matters to not endanger the worker’s safety. Therefore, using measuring tools is in order so that one can make sure of proper functioning, and compliance with electrical codes and standards. Let’s get to know these tools and their uses.
Multimeter (digital or analog): to measure voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits
Voltage Tester: Also known as voltage detectors or non-contact voltage testers is to determine if a circuit is live without direct contact
Clamp Meter: to measure the electrical current without disconnecting a conductor
Ohmmeter: to measure electrical resistance in circuits, components, and conductors

Insulation Tester (megger): to measure the insulation resistance of wires and cables. Necessary to prevent electrical breakdowns.
Circuit Analyzer: To test circuits for ground faults, open circuits, and short circuits.
Power Quality Analyzer: To look out for voltage fluctuations, harmonics, surges, and other parameters.
Continuity Tester: To test the continuity of electrical circuits and connections and verify correct wiring.
Phase Rotation Tester: to determine the sequence of phases in three-phase electrical systems to make sure of proper wiring and phase and phase sequence in motors, generators, etc.

Ground Resistance Tester: To measure the resistance of ground systems and electrodes and make sure they meet the standards
Tachometer: To measure the rotational speed of motors, generators, and other rotating machinery
LUX Meter: To measure the intensity of light in a given area
Wire Gauge (AWG): Also known as American Wire Gauge, is used to identify the wire diameter
Hopefully, now you have a good overview of the different types of measuring tools that are used in various professions. If you’re starting any of these professions, you might need to buy some of the aforementioned tools and if you’re already a professional, now you have a good sense of what might come to your aid and make your job easier.
FAQs:
What is the most popular type of measuring tool?
Rulers are the most popular type of measuring tool.
How accurate are measuring tools?
The accuracy of measuring tools depends on many factors and high-precision is one of them. Calibration, user technique, and environmental con
Sara
9 April 2024